Getting started with GATorch
To use GATorch simply create a GA object. You can then track the measurements of a pytorch model by simply using attach_model(). With
the latter function you can pass a model to your GA object, which will then measure the energy consumption of the model during each
forward and backward pass.
from GATorch import GA
# Create the profiler object and attach a model to it
ga_measure = GA()
ga_measure.attach_model(model)
Note
Due to Platypus attack Intel RAPL requires root permission for energy readings. In order to run this program with the correct permissions, do NOT make Intel RAPL readable for any user as this introduces vulernability. Instead use Python with sudo instead:
~$ sudo ./.venv/bin/python <script_name>.py
Once the model is attached to the GA object you can simply follow you normal training loop routine. GATorch will take care to create the measurements
in the background. You can then retrieve the measurements at any point.
# Let's try to do a single forward pass and a backward pass
x = torch.zeros([1, 1, 28, 28]).to(device)
y = torch.zeros([1, 10]).to(device)
pred = model(x) # forward
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward() # backward
optimizer.step()
# Now lets print the mean measurements
print(ga_measure.get_mean_measurements())
Retrieving the measurements
To retrieve the different energy consumption measurements you can use either of the following functions:
ga_measure.get_mean_measurements()
ga_measure.get_sum_measurements()
ga_measure.get_full_measurements()
Respectively they will show the mean energy measurement of a forward or backward pass of the model, the sum of all the measurements for each pass and the full list of measurements. The measurements are displayed in Joules.
You can also convert the readings into a pandas.DataFrame.
ga_measure.to_pandas()
NeuralNetwork_forward |
NeuralNetwork_backward |
|---|---|
0.031860 |
0.042359 |
0.042236 |
0.034667 |
To now visualize the results use visualize_data().
ga_measure.visualize_data()
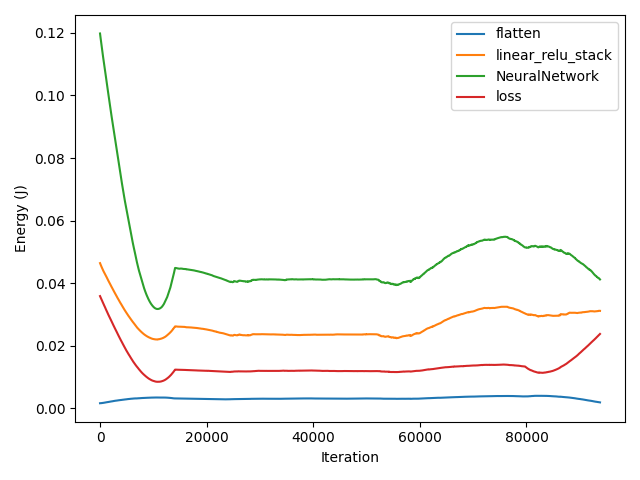
Tracking a model
To start tracking a model you need to attach it to a GA object. By default the GA profiler will also track the energy consumption
that each named layer of the model generates. If you are not intrested in this data you can specify it when attaching the model to the profiler.
ga_measure = GA()
ga_measure.attach_model(model_1, named_layer=False)
If you want to track the energy consumption of a new model you must first detach the previous one. Finally you can also attach a loss function to track the forward and backward passes of the torch loss criterion.
ga_measure.detach_model()
ga_measure.attach_model(model_2, loss=loss_fn)
To reset the current energy measurements use reset().
ga_measure.reset()
Loss vs Energy Consumption
An important feature of GATorch is its ability to compute and display how much energy is needed to improve the loss of a model
at each step of the training loop. This way it is possible to see how improving the loss becomes more expensive as the loss becomes
smaller, giving machine learning scientist and enginners a new criterion to judge, for example, when to stop training. We show this data
using tensorboard.
ga_measure.set_tensorboard_stats()
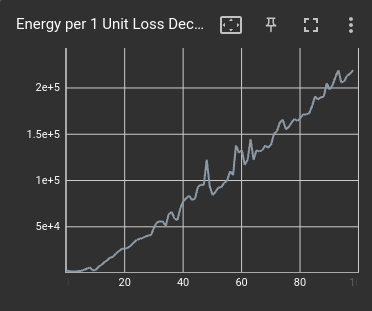
For more details about tensorboard integration see this section.